|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Take a deep breath. Now, imagine that breath isn’t as clean as you’d like. Unfortunately, for many of us, especially in bustling urban centers like Gurugram, this is a daily reality. Air pollution has become a pervasive challenge, affecting not just our lungs and overall health, but often our eyes in ways we might not fully recognize.
If you’ve ever experienced that gritty, burning, or persistently irritated sensation in your eyes, particularly on days when the air quality seems poor, you’re not alone. Your eyes are incredibly sensitive, and they’re often the first part of your body to react to airborne irritants. So, understanding how to protect your eyes from air pollution isn’t just about comfort; it’s about safeguarding your vision and long-term ocular health. At Indira Gandhi Eye Hospitals, we’re deeply committed to helping you understand these environmental challenges and providing you with effective strategies to keep your eyes healthy, comfortable, and clear.
The Unseen Invaders: Understanding Air Pollution’s Impact on Your Eyes
Before we delve into how to protect your eyes from air pollution, let’s first understand what we’re up against. Air pollution isn’t a single entity; it’s a complex mix of solid particles, liquid droplets, and gases floating in our atmosphere. Each component can wreak havoc on your eyes.
Your eyes rely on a delicate tear film, a three-layered shield of mucin, water, and oil, to lubricate, nourish, and protect their surface. This tear film acts as your eye’s first line of defense against the outside world. When exposed to air pollution, this intricate balance is easily disrupted.
Here’s a closer look at the culprits and their effects:
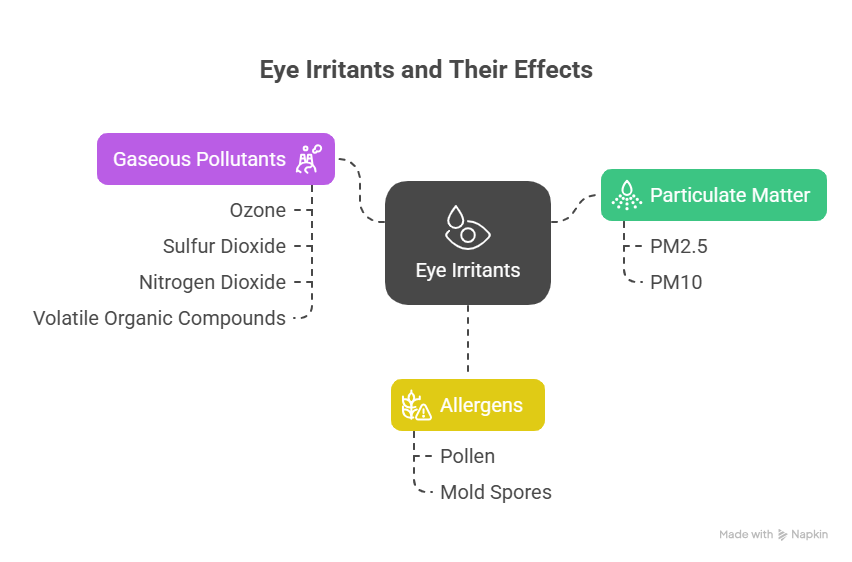
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10):
- These are tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in the air. PM10 (particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter) includes dust, pollen, and mold spores. PM2.5 (particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter) are even finer, originating from combustion sources like vehicles, power plants, industrial emissions, and even residential burning.
- Impact on Eyes: These microscopic particles can directly lodge on the eye’s surface or within the tear film, causing physical irritation, abrasions to the delicate corneal surface, and a persistent “foreign body” sensation. They can also get trapped under contact lenses, leading to severe discomfort and potential damage. The smaller PM2.5 particles can cause more significant inflammation because they can penetrate deeper into tissues.
- These are tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in the air. PM10 (particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter) includes dust, pollen, and mold spores. PM2.5 (particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter) are even finer, originating from combustion sources like vehicles, power plants, industrial emissions, and even residential burning.
- Gaseous Pollutants:
- Ozone (O3): A key component of smog, ozone is formed when pollutants from cars, power plants, and other sources react chemically in the presence of sunlight. It’s a highly reactive gas.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): These gases are primarily released from the burning of fossil fuels in power plants, industrial facilities, and vehicles.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Emitted from paints, solvents, cleaning supplies, and vehicle exhaust.
- Impact on Eyes: Gaseous pollutants are chemical irritants. When they come into contact with the moist surface of your eyes, they can react to form acids, causing chemical burns, redness, stinging, burning, and severe inflammation. They can directly damage the cells on the surface of the eye and disrupt the stability of the tear film, leading to rapid tear evaporation.
- Ozone (O3): A key component of smog, ozone is formed when pollutants from cars, power plants, and other sources react chemically in the presence of sunlight. It’s a highly reactive gas.
- Allergens (Pollen, Mold Spores):
- While not strictly “pollution” in the industrial sense, airborne allergens are often concentrated in polluted air, which can exacerbate their effects. Pollution particles can even carry allergens deeper into the respiratory system and onto the ocular surface.
- Impact on Eyes: Triggering allergic conjunctivitis, leading to intense itching, redness, swelling, and watery discharge. This inflammation further compromises the eye’s natural defenses.
- While not strictly “pollution” in the industrial sense, airborne allergens are often concentrated in polluted air, which can exacerbate their effects. Pollution particles can even carry allergens deeper into the respiratory system and onto the ocular surface.
The Symphony of Symptoms:
When your eyes are exposed to this cocktail of pollutants, they react in various ways. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Irritation: The most immediate and visible sign.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Especially noticeable in gaseous pollution.
- Gritty or Foreign Body Sensation: As if something is constantly in your eye.
- Excessive Tearing: The eye’s attempt to wash away irritants, though often ineffective if the tear quality is poor.
- Dry Eye Symptoms: Paradoxically, pollution often causes or worsens dry eye. The irritants disrupt the tear film’s stability, leading to rapid evaporation and the characteristic symptoms of dryness (soreness, blurred vision, feeling of tired eyes).
- Light Sensitivity (Photophobia): Inflamed eyes become more sensitive to light.
- Blurry Vision: Due to tear film instability or corneal surface damage.
- Allergic Reactions: Persistent itching, swelling of eyelids.
Long-Term Implications: More Than Just Temporary Discomfort
The impact of air pollution on your eyes isn’t always temporary. Chronic exposure can lead to more serious, long-term issues:
- Chronic Dry Eye Disease: Repeated damage to the tear film and ocular surface can lead to a persistent, clinical dry eye condition requiring ongoing management.
- Increased Risk of Ocular Surface Diseases: Chronic inflammation can make the eyes more susceptible to conditions like blepharitis (eyelid inflammation) and conjunctivitis (pink eye).
- Corneal Damage: Repeated abrasion from particulate matter or chemical irritation can lead to micro-erosions on the cornea, increasing the risk of infection and affecting vision quality.
- Exacerbation of Existing Conditions: For individuals already suffering from dry eye, allergies, or other ocular surface conditions, air pollution acts as a significant aggravator.
- Potential Systemic Effects: While direct links to severe sight loss are less clear for environmental air pollution, research is ongoing into subtle long-term effects on deeper ocular structures due to systemic inflammation from pollution.
Protect Your Eyes from Air Pollution
Constant exposure to polluted air can lead to dryness, irritation, and long-term eye problems. Learn effective ways to shield your vision from harmful pollutants.
Get Pollution Protection Tips from Experts

