|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Receiving a diagnosis of glaucoma can naturally bring about a mix of emotions – perhaps concern, a desire for knowledge, and a strong motivation to do everything possible to protect your vision. Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that damages the optic nerve, the vital cable transmitting visual information from your eye to your brain, often linked to elevated pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure, or IOP). While modern medicine offers powerful treatments like eye drops, laser procedures, and surgery to manage glaucoma, many patients also wonder if their daily habits, particularly their diet, can play a role.
The good news is, you’re on the right track! While no food or diet can cure glaucoma or replace your prescribed medical treatment, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including thoughtful dietary choices, can certainly be a valuable complementary strategy. Your diet can influence overall eye health, inflammation, blood flow, and even potentially intraocular pressure. Today, we’re going to delve into what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods, or at least limit, and explore the reasoning behind these recommendations. This isn’t about restrictive diets, but rather about making informed choices to support your eyes and overall well-being. At Indira Gandhi Eye Hospitals, we believe in providing comprehensive care that encompasses not just medical treatment but also practical, empowering advice for your daily life.
Understanding Glaucoma and the Role of Diet
To understand why certain dietary choices might be beneficial or detrimental, it’s helpful to briefly revisit what glaucoma entails. Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy, meaning there’s ongoing damage to the optic nerve. This damage often (but not always) correlates with high intraocular pressure (IOP). The goal of glaucoma treatment is to lower IOP and/or protect the optic nerve to prevent further vision loss.
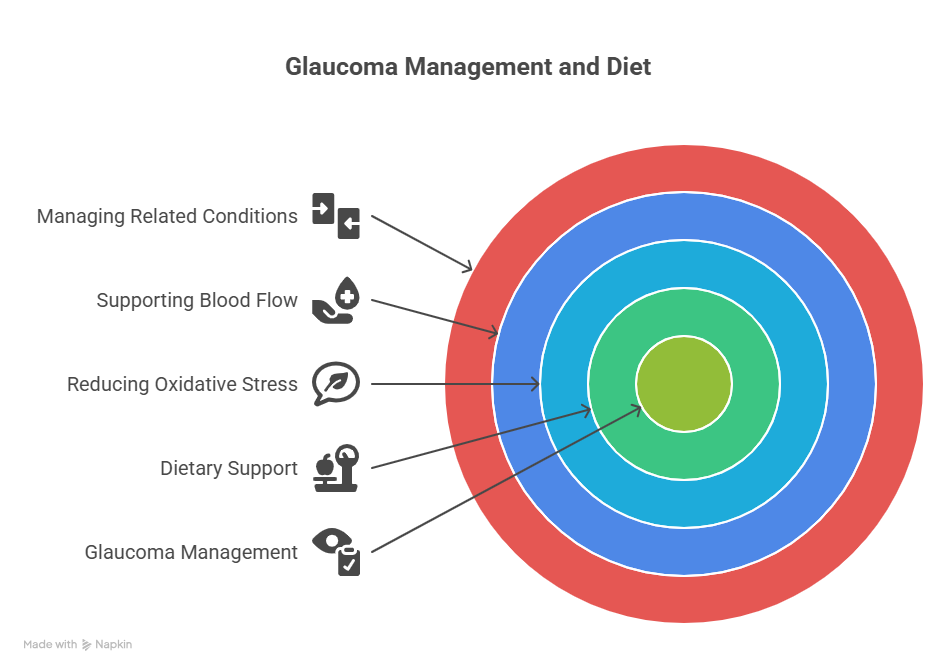
When we talk about diet in the context of glaucoma, we’re discussing a supportive role. A balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help by:
- Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: These processes are believed to contribute to optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds found in food can help combat them.
- Supporting Healthy Blood Flow: The optic nerve needs a robust blood supply to function properly. A diet that supports cardiovascular health can ensure optimal blood flow to the eye.
- Potentially Modulating IOP: While no food dramatically lowers IOP, some dietary components can have subtle effects on fluid dynamics or blood pressure, which can indirectly influence eye pressure.
- Managing Related Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure are risk factors for glaucoma. Dietary choices that help manage these conditions can indirectly benefit glaucoma management.
It’s crucial to reiterate: Dietary changes alone cannot replace your prescribed eye drops, laser treatments, or surgery. These medical interventions are the primary tools for managing glaucoma and preventing blindness. Always discuss any significant dietary changes with your ophthalmologist and potentially a registered dietitian.
Living with Glaucoma? Protect your vision today!
The right diet and timely eye check-ups can slow down vision loss. Don’t wait—consult our specialists now and safeguard your eyesight.
Book Glaucoma Check-UpFoods to Consider Limiting or Avoiding: Why Glaucoma Patients Should Avoid These Foods
When looking at what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods, the focus isn’t necessarily on direct harm from a single food item. Instead, it’s about patterns of consumption that might exacerbate risk factors, promote inflammation, or negatively impact overall health, which in turn could subtly influence eye health.
- High-Caffeine Beverages (Coffee, Energy Drinks, Some Teas):
- Reasoning: Research on caffeine and glaucoma is mixed and ongoing, but some studies suggest that consuming large amounts of caffeine (e.g., more than 2-3 cups of coffee per day) may lead to a transient, short-term increase in intraocular pressure in some individuals. This effect is thought to be related to changes in blood flow and aqueous humor (the fluid inside the eye) production or drainage. For individuals with certain types of glaucoma (e.g., pseudoexfoliation glaucoma) or those who are “caffeine responders,” this temporary spike could be a concern. Furthermore, excessive caffeine intake can sometimes contribute to dehydration, which is generally not ideal for overall health or fluid balance.
- Practical Advice: It’s not usually necessary for Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods entirely when it comes to caffeine, but moderation is key. If you consume a lot of caffeine, consider reducing your intake gradually. Pay attention to how your eyes feel and discuss your caffeine habits with your ophthalmologist. They might recommend measuring your IOP after caffeine intake if there’s a concern. Opting for decaffeinated alternatives or herbal teas can be good choices.
- Reasoning: Research on caffeine and glaucoma is mixed and ongoing, but some studies suggest that consuming large amounts of caffeine (e.g., more than 2-3 cups of coffee per day) may lead to a transient, short-term increase in intraocular pressure in some individuals. This effect is thought to be related to changes in blood flow and aqueous humor (the fluid inside the eye) production or drainage. For individuals with certain types of glaucoma (e.g., pseudoexfoliation glaucoma) or those who are “caffeine responders,” this temporary spike could be a concern. Furthermore, excessive caffeine intake can sometimes contribute to dehydration, which is generally not ideal for overall health or fluid balance.
- High-Sodium Foods (Processed Foods, Canned Goods, Fast Foods, Salty Snacks):
- Reasoning: High sodium intake is directly linked to elevated blood pressure. While the direct link between dietary sodium and IOP isn’t as strong as that with blood pressure, consistently high blood pressure can strain the delicate blood vessels throughout the body, including those that supply the optic nerve. Impaired blood flow to the optic nerve is a significant concern in glaucoma. Additionally, high sodium can contribute to fluid retention, which, in theory, could subtly influence fluid dynamics within the eye. High-sodium diets also often correlate with diets heavy in processed foods, which lack beneficial nutrients.
- Practical Advice: Reduce your intake of processed and packaged foods, which are often hidden sources of high sodium. Read food labels carefully and choose low-sodium options. Prioritize fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, which are naturally lower in sodium. Season your food with herbs and spices instead of relying heavily on salt. This is one of the key areas where Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods if they are trying to manage their overall health, including eye health.
- Reasoning: High sodium intake is directly linked to elevated blood pressure. While the direct link between dietary sodium and IOP isn’t as strong as that with blood pressure, consistently high blood pressure can strain the delicate blood vessels throughout the body, including those that supply the optic nerve. Impaired blood flow to the optic nerve is a significant concern in glaucoma. Additionally, high sodium can contribute to fluid retention, which, in theory, could subtly influence fluid dynamics within the eye. High-sodium diets also often correlate with diets heavy in processed foods, which lack beneficial nutrients.
- Foods High in Saturated and Trans Fats (Deep-Fried Foods, Fast Food, Fatty Red Meats, Baked Goods, Margarine):
- Reasoning: Diets high in unhealthy fats, particularly trans fats and excessive saturated fats, are known to promote systemic inflammation and oxidative stress within the body. They also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing them and impairing blood flow. Optimal blood flow to the optic nerve is crucial for its health and function. Any reduction in this vital blood supply can exacerbate optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Chronic inflammation also plays a role in the progression of many chronic diseases, including potentially glaucoma.
- Practical Advice: Limit your consumption of deep-fried foods, commercially baked goods, and fatty cuts of red meat. Opt for lean protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, and lentils. Choose healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds. Look for “trans fat-free” on food labels. This is a general healthy eating recommendation that specifically benefits individuals with glaucoma because of its impact on inflammation and blood flow, making it important for what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods.
- Reasoning: Diets high in unhealthy fats, particularly trans fats and excessive saturated fats, are known to promote systemic inflammation and oxidative stress within the body. They also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing them and impairing blood flow. Optimal blood flow to the optic nerve is crucial for its health and function. Any reduction in this vital blood supply can exacerbate optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Chronic inflammation also plays a role in the progression of many chronic diseases, including potentially glaucoma.
- Highly Processed Foods and Refined Sugars (Sugary Drinks, Candies, White Bread, Pastries, Breakfast Cereals):
- Reasoning: These foods cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, contributing to systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. For individuals with diabetes, or those at risk of developing diabetes, managing blood sugar is paramount, as diabetes itself is a significant risk factor for glaucoma (especially neovascular glaucoma). Even without diabetes, a diet high in refined sugars and processed foods can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation throughout the body, which is detrimental to overall health and could indirectly affect ocular health. They also tend to be low in essential nutrients.
- Practical Advice: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Choose whole grains over refined grains. Satisfy your sweet tooth with natural sugars from fruits. Limit sugary beverages, candies, and baked goods. This dietary modification contributes to overall metabolic health, which is beneficial for managing glaucoma, making it a critical consideration for what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods.
- Reasoning: These foods cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, contributing to systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. For individuals with diabetes, or those at risk of developing diabetes, managing blood sugar is paramount, as diabetes itself is a significant risk factor for glaucoma (especially neovascular glaucoma). Even without diabetes, a diet high in refined sugars and processed foods can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation throughout the body, which is detrimental to overall health and could indirectly affect ocular health. They also tend to be low in essential nutrients.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption:
- Reasoning: While some studies suggest that very moderate alcohol consumption might have a transient, short-term lowering effect on IOP, excessive and chronic alcohol intake is generally detrimental to health. It can lead to dehydration, deplete essential nutrients (especially B vitamins and antioxidants), and contribute to systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. Long-term heavy drinking can also damage the liver and other organs, indirectly impacting overall systemic health and potentially exacerbating vascular issues that could affect the eyes.
- Practical Advice: If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation (e.g., up to one drink per day for women, and up to two drinks per day for men, or as advised by your doctor). It’s crucial to consult your ophthalmologist about alcohol consumption, especially if you are on any medications for glaucoma, as there might be interactions. For some, complete avoidance might be recommended. When considering what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods for optimal health, alcohol in excess fits the bill.
- Reasoning: While some studies suggest that very moderate alcohol consumption might have a transient, short-term lowering effect on IOP, excessive and chronic alcohol intake is generally detrimental to health. It can lead to dehydration, deplete essential nutrients (especially B vitamins and antioxidants), and contribute to systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. Long-term heavy drinking can also damage the liver and other organs, indirectly impacting overall systemic health and potentially exacerbating vascular issues that could affect the eyes.
Living with Glaucoma? Protect your vision today!
The right diet and timely eye check-ups can slow down vision loss. Don’t wait—consult our specialists now and safeguard your eyesight.
Book Glaucoma Check-UpThe Power of What You Should Eat: Complementary Dietary Strategies
While focusing on what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods is important, it’s equally, if not more, empowering to focus on what you should include in your diet. An anti-inflammatory, antioxidant-rich diet can be a powerful ally in supporting your eye health.
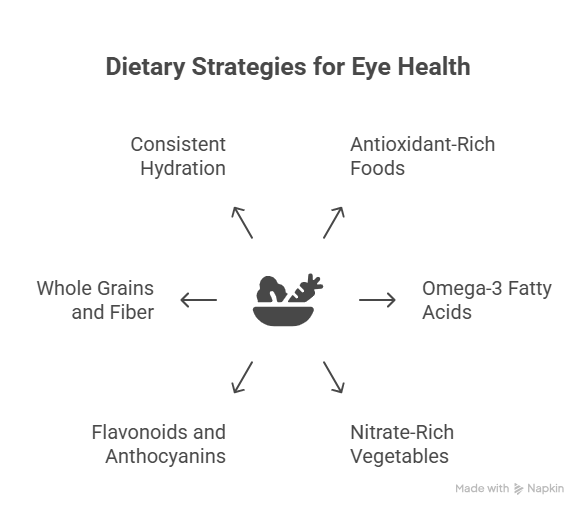
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: These compounds help combat oxidative stress, which is implicated in optic nerve damage.
- Sources: Abundant in colorful fruits and vegetables. Think dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens), berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, and sweet potatoes.
- Specifics: Pay attention to vitamins A, C, and E, as well as carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin (found in leafy greens, corn, eggs).
- Sources: Abundant in colorful fruits and vegetables. Think dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens), berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, and sweet potatoes.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s are crucial for overall cellular health, including nerve cells, and can support healthy blood vessel function.
- Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources. Plant-based sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources. Plant-based sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Nitrate-Rich Vegetables: These vegetables contain nitrates that the body converts into nitric oxide, a compound that helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow. Good circulation is vital for the optic nerve.
- Sources: Beets, spinach, kale, arugula, and other leafy green vegetables.
- Sources: Beets, spinach, kale, arugula, and other leafy green vegetables.
- Flavonoids and Anthocyanins: These plant compounds offer strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Sources: Berries (especially dark ones like blueberries and blackberries), grapes, red wine (in moderation if approved by doctor), dark chocolate (in moderation).
- Sources: Berries (especially dark ones like blueberries and blackberries), grapes, red wine (in moderation if approved by doctor), dark chocolate (in moderation).
- Whole Grains and Fiber: These promote stable blood sugar levels, support gut health, and contribute to overall metabolic well-being, indirectly benefiting ocular health.
- Sources: Oats, brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread.
- Sources: Oats, brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread.
- Consistent Hydration: While avoiding rapid, large fluid intake (which can transiently spike IOP), maintaining consistent, moderate hydration throughout the day is crucial for overall bodily function and tear film health.
Living with Glaucoma? Protect your vision today!
The right diet and timely eye check-ups can slow down vision loss. Don’t wait—consult our specialists now and safeguard your eyesight.
Book Glaucoma Check-UpBeyond Diet: Holistic Glaucoma Management
It is vital to reiterate that while dietary considerations are valuable, they are complementary to, not a replacement for, medical management of glaucoma. The primary treatment for glaucoma involves:
- Prescription Eye Drops: These are the most common first-line treatment, working to either reduce fluid production in the eye or improve its drainage.
- Laser Procedures: Such as Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) or Laser Iridotomy, aimed at improving fluid drainage.
- Surgery: Procedures like trabeculectomy or drainage device implantation are performed in more advanced cases or when other treatments are insufficient to control IOP.
- Regular Comprehensive Eye Examinations: Adhering to your ophthalmologist’s recommended follow-up schedule is crucial to monitor IOP, optic nerve health, and visual fields, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment.
- Lifestyle Factors: Beyond diet, regular moderate exercise, managing stress, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight also play significant roles in overall health and can indirectly support glaucoma management.
Always maintain open communication with your ophthalmologist about your diet and any lifestyle changes you plan to make. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific type of glaucoma, overall health, and treatment plan.
Your Vision, Our Priority: Expert Care at Indira Gandhi Eye Hospitals
Living with glaucoma is a journey that requires vigilance and proactive management. Understanding what Glaucoma Patients should avoid these foods and embracing a nutrient-rich, balanced diet can be a powerful tool in your overall strategy to protect your vision. While diet supports eye health, it’s the consistent and expert medical care that truly keeps this condition under control.
At Indira Gandhi Eye Hospitals, our dedicated team of experienced ophthalmologists specializes in the comprehensive diagnosis and management of glaucoma. We are equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic technologies to detect the disease early and offer a full spectrum of advanced treatments, from innovative medical therapies to sophisticated surgical procedures. We believe in empowering our patients with knowledge and providing compassionate, individualized care that combines the best of modern medicine with practical lifestyle advice.
If you or a loved one are managing glaucoma, or if you have concerns about your eye health, we encourage you to seek expert advice. For a comprehensive eye examination, personalized guidance, and advanced treatment options, we invite you to connect with us. Visit our website at https://indiragandhiehospital.com/ to learn more or to schedule an appointment. Let Indira Gandhi Eye Hospitals be your trusted partner in safeguarding your precious vision.
Living with Glaucoma? Protect your vision today!
The right diet and timely eye check-ups can slow down vision loss. Don’t wait—consult our specialists now and safeguard your eyesight.
Book Glaucoma Check-UpFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is there a specific diet that can cure glaucoma?
No, currently there is no specific diet that can cure glaucoma or replace medical treatments like eye drops or surgery. Dietary changes are considered a complementary strategy to support overall eye health and may help manage risk factors, but they are not a substitute for professional medical care.
Why should glaucoma patients be mindful of caffeine intake?
Some studies suggest that high caffeine intake might cause a transient, short-term increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) in some individuals. While not definitive for everyone, it’s prudent for glaucoma patients to consume caffeine in moderation and discuss their intake with their ophthalmologist.
How do foods high in saturated fats or refined sugars affect glaucoma?
Foods high in unhealthy fats and refined sugars can promote systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, and may contribute to conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes, which are risk factors for glaucoma. These effects can indirectly impact the health of the optic nerve and its blood supply.
Are there any foods that are particularly beneficial for glaucoma patients?
Yes, a diet rich in antioxidants (found in leafy greens, berries, colorful fruits/vegetables), omega-3 fatty acids (from fatty fish, flaxseeds), and nitrate-rich vegetables (like beets and spinach) can support overall eye health, reduce inflammation, and potentially improve ocular blood flow.
Should I completely avoid all the foods mentioned, or just limit them?
For most individuals, the recommendation is to limit or consume these foods in moderation rather than complete avoidance. The focus should be on adopting a balanced, nutrient-dense diet overall. Always discuss specific dietary restrictions or significant changes with your ophthalmologist or a registered dietitian.
Does staying hydrated help with glaucoma management?
Yes, maintaining consistent, moderate hydration throughout the day is important for overall health and supports proper bodily functions, including fluid balance. However, avoid drinking very large volumes of fluid rapidly, as this can sometimes cause a temporary increase in intraocular pressure in some individuals.